Types of Combustion Chamber: Functions, Advantages & Disadvantages (Complete Details)
🔧Types of Combustion Chamber: Functions, Advantages & Disadvantages (Complete Details)
Types of Combustion Chamber
What is Combustion Chamber?
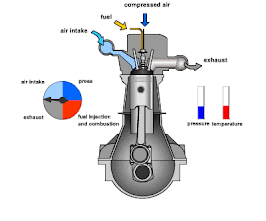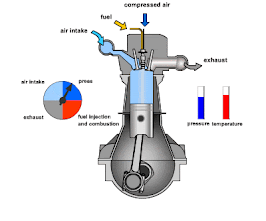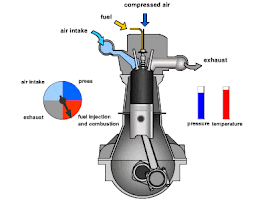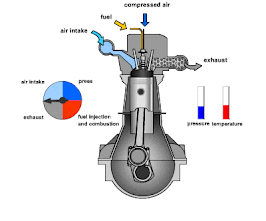
The combustion chamber is a critical component of an internal combustion engine, where the fuel-air mixture is ignited to produce the energy that powers the engine. It's essentially the space within the engine where the combustion process occurs, converting chemical energy into mechanical energy.
Functions of Combustion Chamber summary
The combustion chamber in an internal combustion engine has the following key functions:
- Fuel-Air Mixture Containment: It confines the fuel-air mixture for efficient combustion.
- Energy Conversion: Converts the chemical energy from fuel into mechanical energy by igniting the mixture, causing an explosion that drives the piston.
- Pressure Generation: The explosion generates high pressure that pushes the piston down, driving the engine.
- Compression: Compresses the fuel-air mixture for more efficient combustion, enhancing engine power and efficiency.
- Emission Control: Its design influences the efficiency of combustion, impacting fuel consumption and reducing harmful emissions.
1)Hemispherical (Hemi) Chamber:
- Shape: Dome-shaped.
- Advantages: Efficient airflow, high power output.
- Usage: High-performance engines.
2)Pent-Roof Chamber:
- Shape: Sloped sides forming a pentagon.
- Advantages: Enhanced air/fuel mixture flow, supports multiple valves.
- Usage: Modern, high-efficiency engines.
3)Wedge Chamber:
- Shape: Wedge-like.
- Advantages: Simple design, good for small engines.
- Usage: Various engine types, especially older models.
4)Open Chamber:
- Shape: Simple, open design.
- Advantages: Efficient combustion, lower emissions.
- Usage: Modern engines with a focus on emissions control.
- Shape: More complex, with contours to control flow.
- Advantages: Better control of combustion and mixture.
- Usage: Engines designed for performance and efficiency.






![🔧💡Types of Fuel Injector – Working, Uses, Parts & Diagram [Complete Details]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/a/AVvXsEi2OzpiTESeIeOQLp_pGkwh1C0Tyaq3nGxeeusC6ucnpR1xZDAudf5CmHm0DLq7T-zHEnDs1onUKsZwX-qf_BdexWUvaPLxjiApsZZ_FQWFO0HWi7wxUWpEpPb4fn9ER22YSUc5NsrTWnSjjvyqVbQOZb2aOiRgOJ5WICRQQH00FD9mE8si-TvbZvKzto0N=w644-h286)



